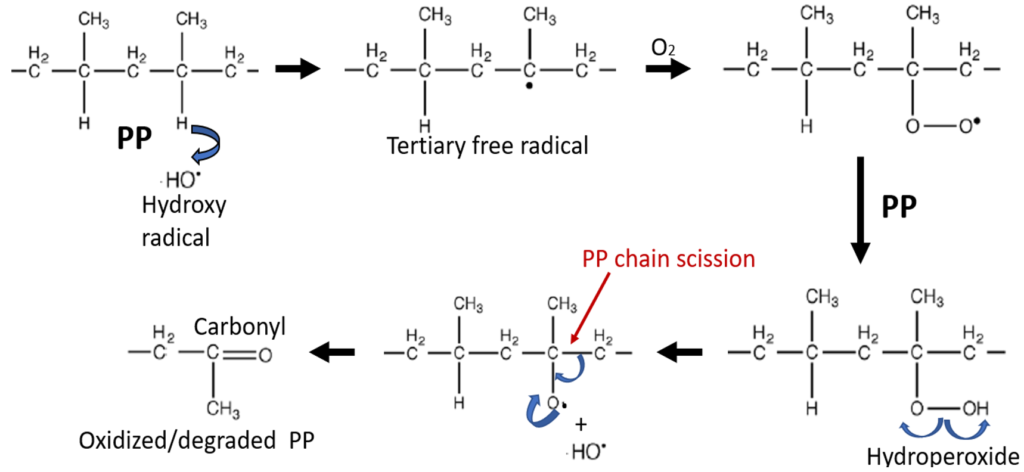
The most common cause of plastic parts to weaken is exposure of the plastic to sunlight. Plastics consist of long polymer chain molecules which are entangled together, The longer the polymer chains, the stronger the plastic
A CASE STUDY
The following case study is the property of Plastic Expert Group and cannot be copied or distributed without prior permission. Our case analysis does not imply that this specific plastic failure will happen systematically. Every case is unique and should be treated accordingly.
PROBLEM: HOW DOES PLASTIC DECOMPOSE?
Plastics consist of long chain molecules. The links that form the chain determine how the plastic decomposes. There are many ways that plastics decompose including oxidation, hydrolysis, and pyrolysis (heating the plastic to very high temperature causing the polymer chains to unzip back to monomer). Pyrolysis is a method that is being used to convert plastics back to a liquid that can be used as fuel. If the plastic contains carbonate links (for example, polycarbonate (PC), or ester links (for example polyethylene terephthate (PET) in the polymer chain, the plastics can decompose by hydrolysis. Most plastics contain carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bonds. C-H bonds are reactive toward oxygen in the air, especially when heated in air or when exposed to sunlight. When the C-H bonds react with oxygen, the polymer chains break causing the plastic to degrade, weaken, and become brittle.